White Tail Deer Doe: Essential Facts and Habitat Insights
White Tail Deer Doe are fascinating creatures found across North America. They are known for their grace and adaptability.
White tail deer does play a vital role in the ecosystem. These gentle animals help maintain forest health and balance. They are a key part of the food chain. Understanding their behavior and habits can enhance our appreciation of nature.
From their unique markings to their nurturing instincts, white tail deer does offer much to discover. Their presence in the wild is both a sign of a healthy environment and a beautiful sight for nature lovers. Join us as we explore the world of white tail deer does, uncovering their secrets and highlighting their importance in the natural world.
Introduction To White Tail Deer Doe
The White Tail Deer Doe is a fascinating creature that roams the forests and fields of North America. Known for its grace and beauty, the doe plays a crucial role in the ecosystem. This introduction will provide an insight into its unique characteristics and its significance in nature.
Characteristics
The White Tail Deer Doe is easily recognizable by its white-tipped tail, which it raises as a warning signal. Here are some key characteristics:
- Size: Adult does typically weigh between 90-200 pounds.
- Color: They have a reddish-brown coat in summer and a grayish-brown coat in winter.
- Antlers: Unlike bucks, does do not have antlers.
- Speed: They can run up to 30 miles per hour to escape predators.
- Diet: Their diet includes leaves, twigs, fruits, and nuts.
Significance
White Tail Deer Does hold immense significance in the ecosystem. Here’s why:
- Population Control: They help maintain the balance of plant species by grazing.
- Food Source: They are a vital food source for predators such as wolves and cougars.
- Seed Dispersion: By consuming fruits, they aid in the dispersion of seeds.
- Indicator Species: Their health reflects the overall health of the ecosystem.
Understanding the White Tail Deer Doe’s characteristics and significance helps us appreciate these majestic animals and their role in nature.
Physical Appearance
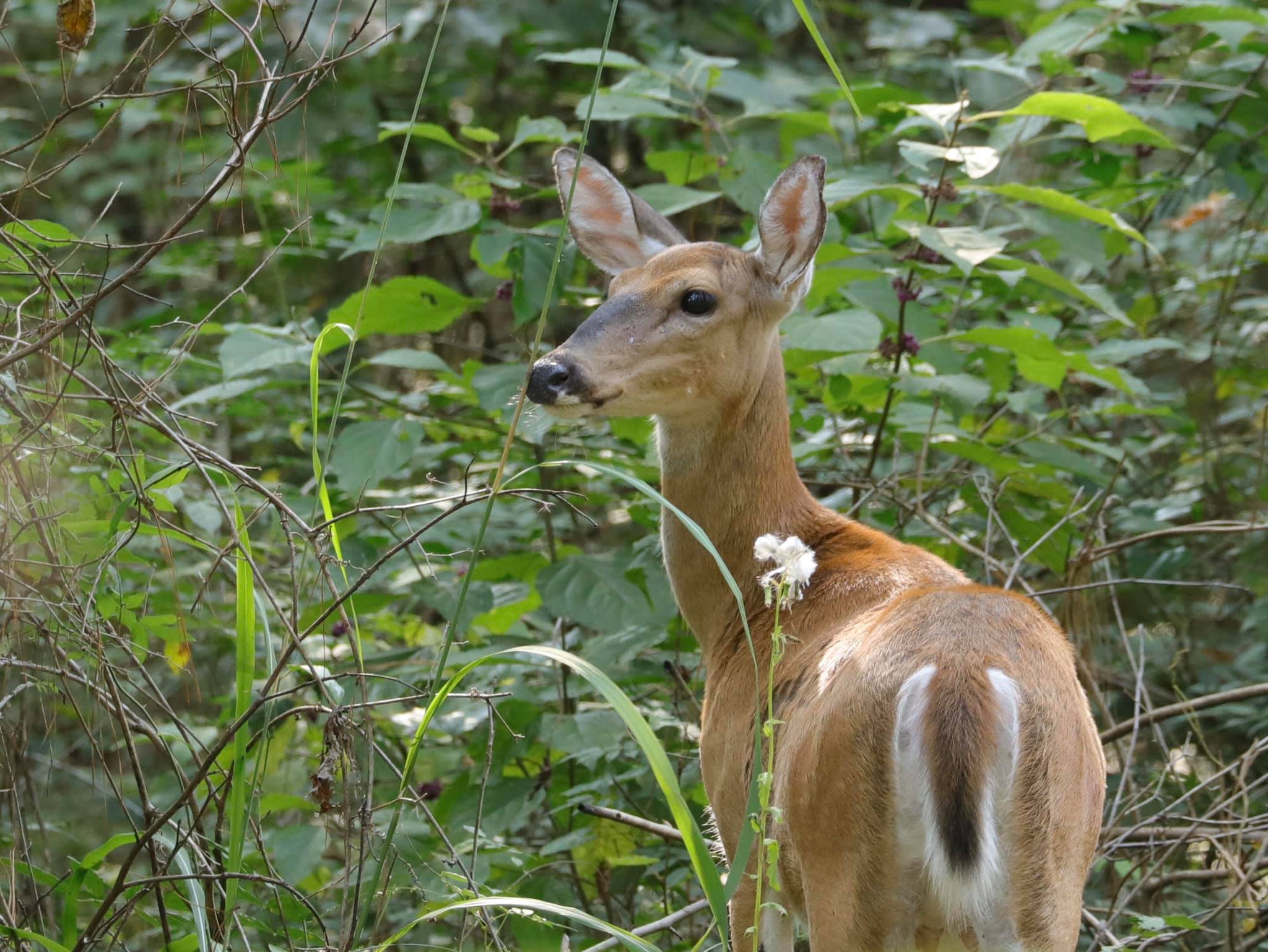
The physical appearance of a White Tail Deer Doe is unique and graceful. They are known for their slender bodies and alert posture. This makes them easily recognizable in the wild. Their physical traits help them survive and thrive in their natural habitat.
Size And Weight
A White Tail Deer Doe is usually smaller than a buck. They weigh between 90 and 130 pounds. Their body length ranges from 5 to 6 feet. The average height at the shoulder is about 3 feet. These measurements vary by region and food availability.
Coloration And Markings
The coloration of a White Tail Deer Doe changes with the seasons. In summer, their coat is reddish-brown. This helps them blend in with the lush vegetation. During winter, their coat turns grayish-brown. This provides better camouflage in the snowy landscape.
White Tail Deer Does have distinct markings. A white patch can be seen on their throat. They also have a white ring around their eyes and nose. The most notable feature is their white under-tail. This is visible when they raise their tail as a warning signal.
Behavioral Traits
The behavioral traits of a White Tail Deer Doe are fascinating. These gentle creatures exhibit unique behaviors that help them survive and thrive in their environment. Let’s explore some of their key behavioral traits.
Social Structure
White Tail Deer Does have a well-defined social structure. They live in small groups known as family units. These groups usually include a few does and their fawns. The family unit provides safety and support for each other.
Within these groups, there is a clear hierarchy. Older does generally lead the group. The hierarchy helps maintain order and ensures the group’s well-being. During the fawning season, does often separate from the group to give birth and care for their fawns in isolation.
Communication Methods
White Tail Deer Does use various methods to communicate. These methods include vocalizations, body language, and scent marking. Each method serves a different purpose and helps them interact with each other effectively.
| Communication Method | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Vocalizations | Alert others about danger or locate each other. |
| Body Language | Show dominance or submission. |
| Scent Marking | Mark territory and signal reproductive status. |
Vocalizations include grunts, bleats, and snorts. Grunts are used to maintain contact with fawns. Bleats are common between does and their young. Snorts often signal danger.
Body language involves tail movements and ear positions. A raised tail can indicate alarm. Ears pointing forward show attentiveness. A relaxed posture suggests calmness.
Scent marking helps establish territory. It also plays a role in mating. Does use scent glands to leave their mark, signaling their presence to other deer.
Diet And Feeding Habits
White tail deer doe often graze on grasses, shrubs, and leaves. They also enjoy fruits, nuts, and mushrooms. These feeding habits help them stay healthy and strong.
White-tail deer does have diverse diets. Their feeding habits change throughout the year. They need a variety of foods to stay healthy and strong. Let’s explore their preferred foods and seasonal variations.Preferred Foods
White-tail deer does love eating plants. They prefer leaves, fruits, and nuts. They also consume grasses, twigs, and bark. Acorns are a favorite treat. They eat mushrooms too. Their diet is rich in natural vegetation.Seasonal Variations
In spring, they eat young leaves and shoots. Summer brings berries and fruits. Fall is all about acorns and nuts. In winter, food becomes scarce. They rely on twigs and bark. Seasonal changes affect their diet. They adapt to what’s available. “`Breeding And Reproduction
White-tailed deer does have fascinating breeding and reproduction habits. Understanding these habits helps in appreciating their life cycle. Let’s explore the details of their mating season and how they raise their offspring.
Mating Season
The mating season for white-tailed deer does is known as the rut. This period usually occurs from October to December. During this time, bucks become more aggressive and active. They search for does and mark their territory. Does signal their readiness to mate through specific behaviors and scents. Once a doe accepts a buck, mating occurs quickly.
Raising Offspring
After mating, the doe carries the pregnancy for about seven months. The fawns are usually born in late spring or early summer. A doe can give birth to one to three fawns. After birth, the doe hides her fawns to protect them from predators. She visits them to nurse and care for them. Fawns stay hidden and motionless to avoid detection. As they grow stronger, they start to follow their mother. By the fall, they can join the herd.

Credit: www.edkanze.com
Habitat Preferences
White Tail Deer Doe are fascinating creatures known for their adaptability. They thrive in various environments. Understanding their habitat preferences can help us appreciate these animals even more. This section explores the ideal environments and geographic distribution of White Tail Deer Doe.
Ideal Environments
White Tail Deer Doe prefer areas with ample cover and food. They thrive in dense forests, where they can find shelter and avoid predators. They also favor open fields and meadows for grazing. These areas provide a mix of grasses, shrubs, and trees.
Water sources are crucial. Deer often stay near rivers, streams, and lakes. These water bodies offer hydration and support lush vegetation. This vegetation is vital for their diet.
During the winter, they seek areas with less snow. Dense coniferous forests provide a warmer and safer environment. These forests offer protection from the harsh weather and predators.
Geographic Distribution
White Tail Deer Doe are widespread across North America. They are native to the United States, Canada, and Mexico. Their range extends from southern Canada to northern South America.
In the United States, they are most common in the eastern and central regions. States like Pennsylvania, Michigan, and Texas have high populations. They adapt well to different climates, from the cold north to the warmer southern states.
In Canada, they are found in southern regions. Provinces like Ontario and Quebec have significant populations. They are less common in the western parts of the country due to harsher climates.
White Tail Deer Doe have also been introduced to other regions. They now exist in parts of Europe, New Zealand, and the Caribbean. This adaptability shows their incredible resilience and ability to thrive in various environments.
Challenges And Threats
White Tail Deer Doe face many challenges and threats in their natural habitat. Understanding these challenges helps us appreciate their resilience and the importance of their conservation.
Predators
White Tail Deer Doe have several natural predators that pose significant threats to their survival. These include:
- Coyotes: They hunt deer, especially fawns.
- Wolves: Larger packs can take down adult does.
- Bobcats: They typically target younger or weaker deer.
These predators help maintain the balance in the ecosystem by controlling deer populations. Yet, it places constant pressure on deer to stay vigilant and adapt.
Human Impact
Human activities significantly impact White Tail Deer Doe, often disrupting their natural habitats. The main human-related threats include:
- Habitat Loss: Urbanization and agriculture reduce available living space.
- Vehicle Collisions: Roads and highways pose significant dangers.
- Hunting: Regulated hunting can help control populations but also reduces numbers.
Additionally, pollution and climate change affect the availability of food and water sources. Conservation efforts are essential to mitigate these impacts and ensure the survival of White Tail Deer Doe.
Conservation Efforts
White Tail Deer Doe populations face many challenges today. Conservation efforts aim to protect these beautiful creatures. These efforts involve various strategies and community support. Understanding these measures helps us appreciate the work being done.
Protection Strategies
One key strategy involves habitat preservation. Healthy habitats mean healthy deer populations. Conservationists work to restore and maintain natural habitats. This includes planting native vegetation and removing invasive species. Another strategy is regulating hunting. Proper hunting regulations ensure deer populations stay balanced. Wildlife agencies set hunting seasons and limits. They also monitor deer health and numbers. Disease control is also crucial. Deer can spread diseases like Chronic Wasting Disease. Efforts include testing and managing affected deer populations. These strategies together help protect White Tail Deer Doe.
Community Involvement
Community involvement plays a vital role in conservation. Local communities can support habitat restoration projects. Volunteers help plant trees and clean up natural areas. Schools and organizations can educate about deer conservation. They can teach the importance of protecting wildlife. Landowners can also contribute. They can create deer-friendly habitats on their properties. Simple actions like planting native plants make a difference. Reporting deer sightings helps too. This data helps track deer populations and health. Engaging the community fosters a sense of stewardship. Everyone can play a part in protecting White Tail Deer Doe.
Interesting Facts
The white tail deer doe is a fascinating creature. They exhibit unique behaviors and impressive adaptation skills. Here are some interesting facts about these beautiful animals.
Unique Behaviors
White tail deer does have some unique behaviors that set them apart.
- They communicate using body language. Their tails flicker to signal danger.
- Does are very social. They often live in groups called herds.
- During the birthing season, does isolate themselves. This helps protect their fawns.
Adaptation Skills
These does have remarkable adaptation skills.
| Adaptation | Description |
|---|---|
| Camouflage | Their coat changes color with the seasons. |
| Speed | They can run up to 30 miles per hour. |
| Diet | They eat a variety of plants to survive. |
These skills help them thrive in various environments.

Credit: mossyoakgamekeeper.com

Credit: www.nps.gov
Frequently Asked Questions
What Do White Tail Deer Doe Eat?
White tail deer doe eat a variety of plants. Their diet includes leaves, fruits, nuts, and twigs. They also consume grasses and herbs.
How To Identify A White Tail Deer Doe?
A white tail deer doe lacks antlers. They have a slender body and a distinct white underside to their tail.
When Are White Tail Deer Doe Most Active?
White tail deer doe are most active during dawn and dusk. They tend to avoid the midday heat.
Where Do White Tail Deer Doe Live?
White tail deer doe inhabit forests, fields, and wetlands. They prefer areas with dense vegetation for cover.
Conclusion
White Tail Deer Doe are fascinating creatures. They show grace and beauty in nature. Understanding their habits helps us appreciate wildlife more. Watching them can be a peaceful and rewarding experience. Remember to respect their habitat and maintain a safe distance.
This ensures their safety and ours. Observing these deer offers insight into their world. Nature lovers and wildlife enthusiasts will find them intriguing. Enjoy the beauty and tranquility they bring to the environment. White Tail Deer Doe truly enrich our natural surroundings.