Do Deer Eat Prickly Pear Cactus
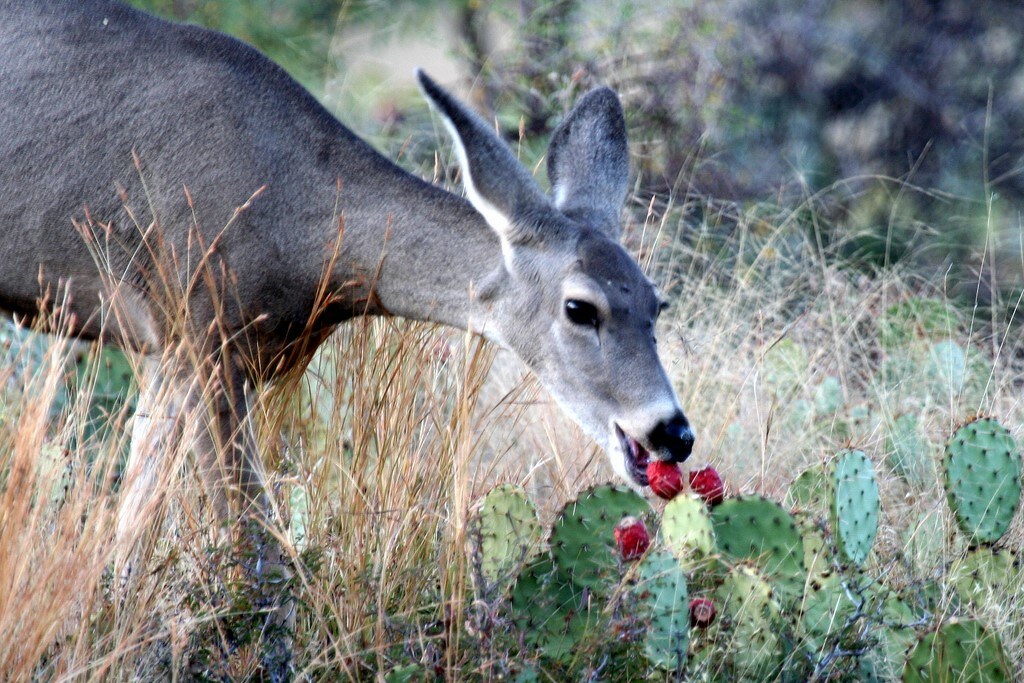
Yes, deer do eat prickly pear cactus. The leaves and pads of the plant are a source of nutrition for them. Deer will nibble on the green parts of the plant in early spring when other food sources are scarce or not yet available.
Prickly pear cacti can also provide shelter from harsh weather conditions and predators, making it an attractive food source for deer. In addition to consuming the edible parts of the plant, deer have been known to rub their antlers against prickly pears and use them as scratching posts to rid themselves of parasites or shed velvet from their antlers each year.
Deer may not be the first animal that comes to mind when you think of prickly pear cactus consumption, but they are actually one of the few mammals that are able to eat this spiky plant. While it may seem unlikely for these graceful animals to enjoy such a sharp-edged food source, deer actively seek out and consume prickly pear cactus when other sources of vegetation become scarce.
Deer eating a prickly pear cactus. A little thorny but seems OK!????
How to Get Rid of Prickly Pear Cactus
One of the best ways to get rid of prickly pear cactus is by using a shovel or hoe to dig up and remove the plant. This will ensure that all parts of the plant are removed, including its root system. Alternatively, you can use Roundup or other weed killers to kill off any remaining portions of the cactus.
To prevent regrowth, it’s important to make sure that no pieces remain in the soil after removal.
Prickly Pear Cactus for Sale
If you’re looking for a unique and interesting plant to add to your garden, consider the prickly pear cactus! This hardy succulent is drought-tolerant and easy to care for, making it an ideal choice for beginner gardeners. Prickly pears feature bright pink or yellow flowers that bloom in summertime and are edible when harvested at the right time.
You can find prickly pear cacti for sale online or in some specialty gardening stores.
Tuna Fruit
Tuna fruit, also known as prickly pear or cactus fruit, is a type of berry that grows on the Opuntia plant. It has a sweet and juicy taste and can be eaten fresh or used to make jellies and jams. The health benefits of tuna fruit include being rich in vitamins A, C, and K as well as minerals such as calcium and magnesium.
Additionally, it contains essential fatty acids which may help reduce inflammation. Its antioxidant properties may even provide protection against certain types of cancer.
Paddle Cactus
The paddle cactus (Opuntia basilaris) is a type of cactus native to the deserts of California and Arizona. It is an incredibly hardy plant that can survive in temperatures ranging from -20°F to over 100°F, and it’s well-adapted for growing in arid environments with minimal water or fertilizer. The paddle cacti have thick, flat stems that are covered in spines, making them recognizable even from a distance.
Furthermore, they produce beautiful white flowers during the summer months that attract bees, butterflies and other pollinators.
Opuntia Humifusa
Opuntia humifusa, commonly known as the Eastern Prickly Pear Cactus, is a flowering perennial cactus native to parts of the United States and Canada. This low-growing cacti typically grows in sandy or gravelly soils and can reach heights of up to 10 inches tall with flattened pads covered in spines. It blooms bright yellow flowers from June through August that are attractive to butterflies and hummingbirds, making it a popular choice for pollinator gardens.

Credit: www.jungledragon.com
What Eats Prickly Pear Cactus?
Many different types of animals eat prickly pear cactus. Some of the most common include desert tortoises, javelinas, deer, antelope, rabbits and mice. They will often peel away the spines to get access to the juicy inner flesh of the plant.
Additionally, some birds such as quails or doves have been known to eat both ripe fruits and pads off prickly pear cacti. Furthermore, a wide range of insects from bees and beetles to moths also feed on this type of cactus in its various forms by piercing through its skin for nourishment.
Is Prickly Pear Cactus Deer Resistant?
Yes, the prickly pear cactus is deer resistant. This is because of its thick exterior and spines which act as a deterrent for deer, making it an ideal choice for those looking to keep their gardens or yards safe from browsing deer. In addition, this type of cactus can survive in both hot and dry climates; meaning that they can generally withstand drought conditions better than other plants which makes them even less appealing to deer.
Lastly, the prickly pear cactus produces fruit with edible pulp – another factor that deters animals such as deer from consuming it.
Can Deers Eat Cactus?
Yes, deers can eat cactus. Cacti are an important food source for deer in certain regions because they provide nutrients and hydration during times of drought or sparse vegetation. While most species of cactus contain sharp spines that make them difficult to consume, some varieties have evolved soft or flat spines that allow deer to eat them more easily.
Additionally, some species contain a sweet pulp inside the plant that is highly palatable to animals such as deer. In areas where there is abundant cactus growth, it is not uncommon for it to be one of the main components in a deer’s diet.
Does a Mule Deer Eat Prickly Pear Cactus?
Yes, mule deer will sometimes consume prickly pear cactus in order to meet their nutritional needs. The pads of the cactus are a source of dietary fiber and can provide them with energy from carbohydrates, as well as vitamins and minerals such as calcium, magnesium, potassium, zinc and iron. However, they may only eat it when other foods are scarce or unavailable due to its spiny nature which can be difficult for them to access without getting hurt.
In addition to consuming the pads of the cactus directly off the plant, mule deer have also been known to eat fallen fruit from some species of prickly pear.
Conclusion
This blog post has definitively demonstrated that deer do indeed eat prickly pear cactus. While it may not be the most common food source for these animals, it is certainly a viable option for them when other vegetation is scarce. Deer have been observed in their natural habitats consuming the fruits and pads of this plant species, indicating that they find the nutritional value beneficial to their health and well-being.
In conclusion, we can conclude that deer are capable of eating prickly pear cactus and may even seek it out if necessary.